Learn more about our Biomedical Services
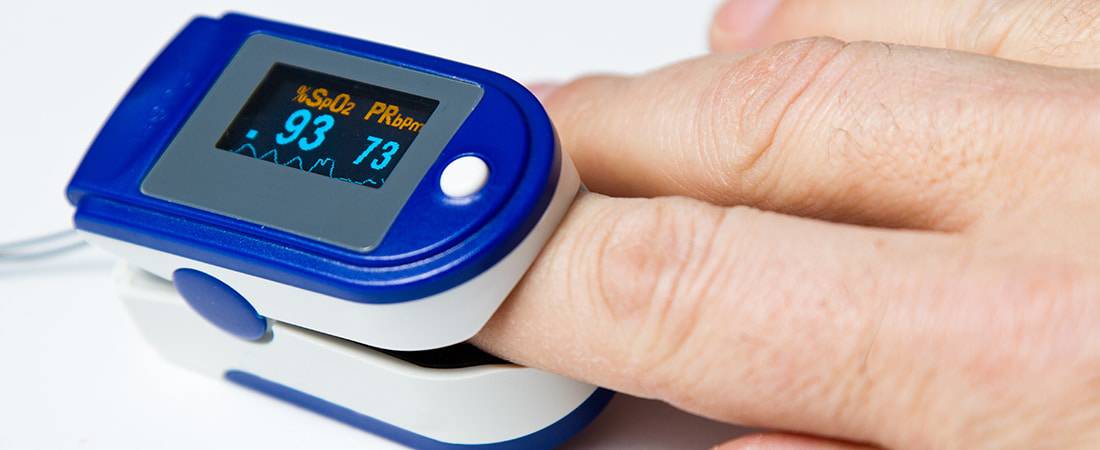
Pulse Oximeter
Terrain Biomedical – Pulse Oximeter – Reconditioned Medical Equipment Sales, Rentals, Service – 773-697-8400
A pulse oximeter is a lightweight, fairly small medical device that is used for monitoring the amount of oxygen that is being carried within the body. A noninvasive item, a pulse oximeter simply attaches comfortably to the patient’s fingertip, directing two wavelengths of light straight through the finger in order to accurately measure the pulse rate as well as how much oxygen is within the patient’s system. After the pulse oximeter is finished with its assessment, its display screen will show the percent of oxygen in the blood coming from the patient’s heart in addition to the current heart rate.
When is a pulse oximeter used?
A pulse oximeter can be used to assess if there is sufficient oxygen in patient’s bloodstream. This useful information is required for a number of different situations such as:
-During or following surgery or other medical procedures where sedation is involved
-To assess how well lung medications are working
-To assess a patient’s ability to sustain increased levels of activity
-To see if a ventilation may be needed to assist with a patient’s breathing, or to assess how effectively a ventilator is working
-To check if a patient has sleep apnea (instances where their breathing stops while they are sleeping)
Pulse oximetry can also be used to evaluate a person’s health if they have a condition that impacts their blood oxygen levels like: anemia, heart attack, asthma, pneumonia, heart failure or lung cancer.
Healthcare providers may have additional reasons to recommend use of a pulse oximeter.
Risks involved in use of a pulse oximeter
All medical procedures carry some degree of risk. The risks involved with use of a pulse oximeter may include: inaccurate reading if the device falls off the fingertip or skin irritation due to the adhesive upon the unit. A patient’s risk can vary based on their general health or other health factors. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of their health and medical background and share any concerns before this or any other type of procedure or test.
Getting prepared for a pulse oximeter application
Healthcare providers will review what to expect during the procedure with their patients. Patients should be certain to ask questions they may have regarding this procedure. If a fingertip unit is to be used for the procedure, the patient might be asked to remove nail polish. Other instructions to prepare may vary according to the patient’s needs.
What takes place during a pulse oximetry session?
This procedure is typically performed as part of an outpatient procedure, although it can be performed during a longer stay in a hospital. The way in which the pulse oximeter procedure is performed can vary. It is dependent upon the patient’s general condition and their healthcare practitioner’s methods. In most instances, pulse oximetry will entail the following process:
A clip-like component – a probe – is placed upon the patient’s fingertip. Alternatively, a probe with an adhesive is placed on the patient’s forehead or earlobe.
The probe can be left in place for continuous monitoring or it might be utilized for just one reading. The probe is removed following the test. Afterwards, the patient is able to return home after their test, unless, naturally, they are in the healthcare facility for additional reasons. They may resume their regular diet and daily activities as per the instructions of their care provider.
Suggestions for Interpreting the Results of a Pulse Oximeter
-Always assess plethysomograph in direct conjunction with SpO2 readout to assure dependability. Oxygen saturation as indicated by the pulse oximeter is assessed utilizing the ratio of Oxygen-Hemoglobin to Deoxy-Hb. This is a helpful piece of information to help evaluate if a patient is capable of transferring oxygen into their bloodstream, although 100 percent saturation displayed by the pulse oximeter is not a guarantee that the patient’s tissues are adequately oxygenated.
-Hemoglobin can typically bind approximately 1.34 mL of Oxygen/g Hb as well as a standard normal Hb of 15 g/dL, which makes the oxygen binding capacities approximately 20 mL Oxygen/dL blood at 100 percent saturation. When concentration of Hb is lower, there is a decline total oxygen content of the blood, but no change in the oxygen saturation, so pulse oximetry is generally not a purely effective test to assess for anemia.
For instance, with a patient who has functioning hemoglobin but with a hemoglobin concentration of eight g/dL the oxygen binding capability is about 10.7 mL Oxygen/dL. Basically, half of the levels of oxygen is getting delivered, but the pulse oximeter display might still show 100 percent. Comparably, in the event a patient tests for hemoglobin molecules that are abnormal, like with a case of sickle cell anemia where oxygen dissociation curves are shifted right, pulse oximeters may not be an accurate measure of an issue such as hypoxemia and may cause over-treatment or over-diagnosis. As a result, arterial blood gas determinations can be more precise for patients who have hemoglobin dissociative curves that are abnormal.
-Pulse oximeters are frequently applied to the patient’s ear lobe or fingertip. Nail polish might throw pulse oximeter readings.
-In a patient who has carbon monoxide poisoning, hemoglobin with abnormal binding has comparable absorption spectrum similar to when oxygen is bound within the ‘R’ configuration. Consequently, pulse oximeters may indicate high saturation levels from to the high amount of hemoglobin within the ‘R’ configuration, but it may be due to the tissues not obtaining adequate oxygen.
To summarize, pulse oximeters are a useful non-invasive medical device that provides information about the percentages of hemoglobin molecules carrying oxygen within the arterial blood of patients who have standard oxygen-dissociative curve readings. Being aware of the values and possible shortcomings of a pulse oximeter will enable healthcare practitioners to gain a better understanding of tissue oxygenation levels of their patients and to be prepared for issuing sound decision regarding treatment.
For patients who have abnormal hemoglobin structures, levels or hemoglobin that is abnormally bound onto other molecules, pulse oximeters will not yield a precise oxygenation reading.
A Look at Terrain Biomedical’s Services
Parts and Accessories: Equipment repair technicians, end users and clinical engineers can each benefit from the broad selection of parts and accessories at Terrain. As among the largest in the nation, we stock the smallest, difficult to find parts to large medical appliances.
We Purchase Medical Equipment: Let us know if you possess medical-related items you’re interested in selling. We purchase significant amounts of preowned medical equipment each year. If you are looking to upgrade to newer, more recent models or you simply wish to unload equipment you do not need any longer, we’re interested in buying your medical equipment.
Consultation and Planning: Our experienced biomedical engineers create a customized plan based on your specific environment, budget applications and preference.
We Sell Equipment: From accessories and parts to certified medical components, our sales practices are supported by engineers who can assist you in choosing the best equipment for your applications.
Installation and Removal: We offer professional installation of new medical equipment. We can also teach your staff how to operate it too. And if you need to open up some space at your facility, we can also help you in removing equipment.